TIMELINE
ART & RITUAL SPACE
200
Salita del Cocomero, Via Latina (Catacomb of Sant’Agnese) early catacomb featuring chapel like space

230
Dura-Europas Church
313
Edict of Milan – makes Christianity legal
325
First Council of Nicea – declared Jesus as Homoousios
337
Christianity becomes the official religion of the Roman Empire

350
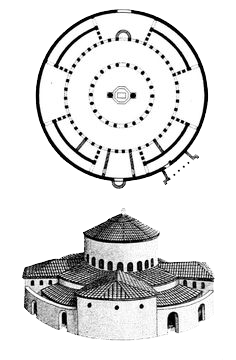
Santa Costanza – Built by Constantine as a Mauseleum
397
Augustine begins writing Confessions
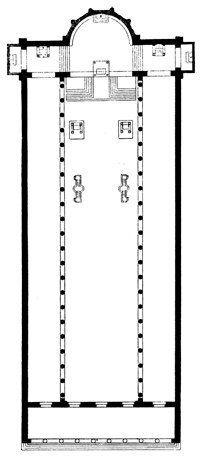
432
Santa Maria Maggiore – early example of Basilica
468
San Stefano Rotondo – example of early martyria
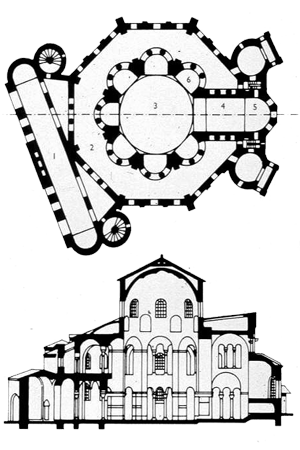
527
San Vitale

532
Hagia Sophia
726
Emperor Leo III attacked the use of images; John of Damascus defended the use of icons
754
Council of Hiereia – use of images condemned
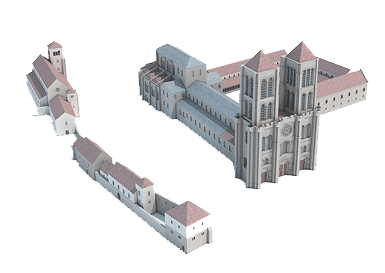
775
Saint-Denis (Romanesque building from 775)
787
Council of Nicea – use of images defended
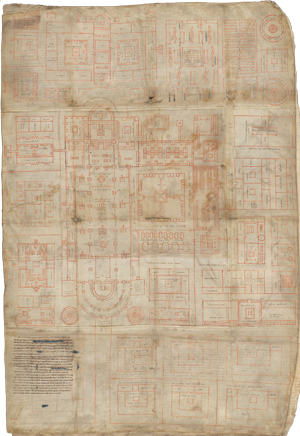
816
Plan of Monastery of Saint Gall, Switzerland
843
Theodora (widow of Emperor Theophilus) restores the use of images in the Orthodox Church
869
Council of Constantinople declared that man is body and soul only
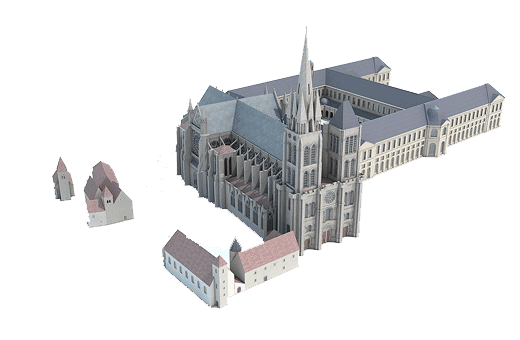
1140
Saint-Denis (Romanesque building from 775)

1194
Chartres Cathedral
1215
4th Lateran Council - Doctrine of Transubstantiation – put more emphasis on the chancel and on the role of the priest
1224
Thomas Aquinas publishes Summa Theologica

1305
Giotto’s Scrovegni Chapel in Paduasan
1471
Capitoline Museums begin with a donation to the city of Rome by the Papacy (the oldest public collection of art in the world)
1472
Basilica of Sant’Andrea, Mantua (Alberti)

1501
Michelangelo begins work on David
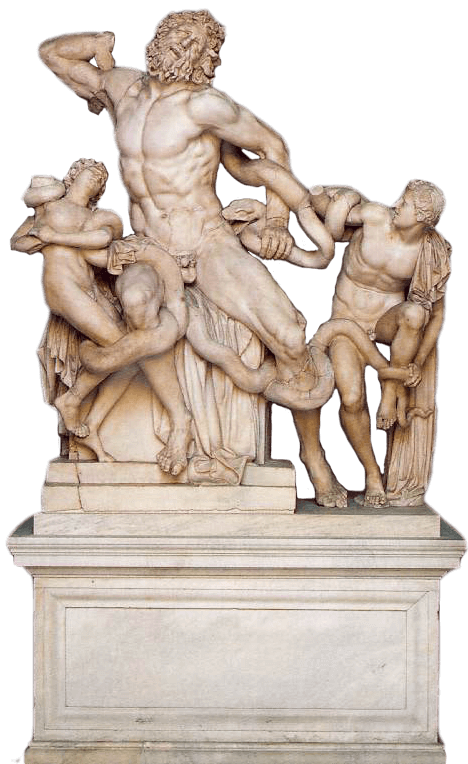
1506
Vatican Museums originate with the purchase of Laocoõn and His Sons and put on public display
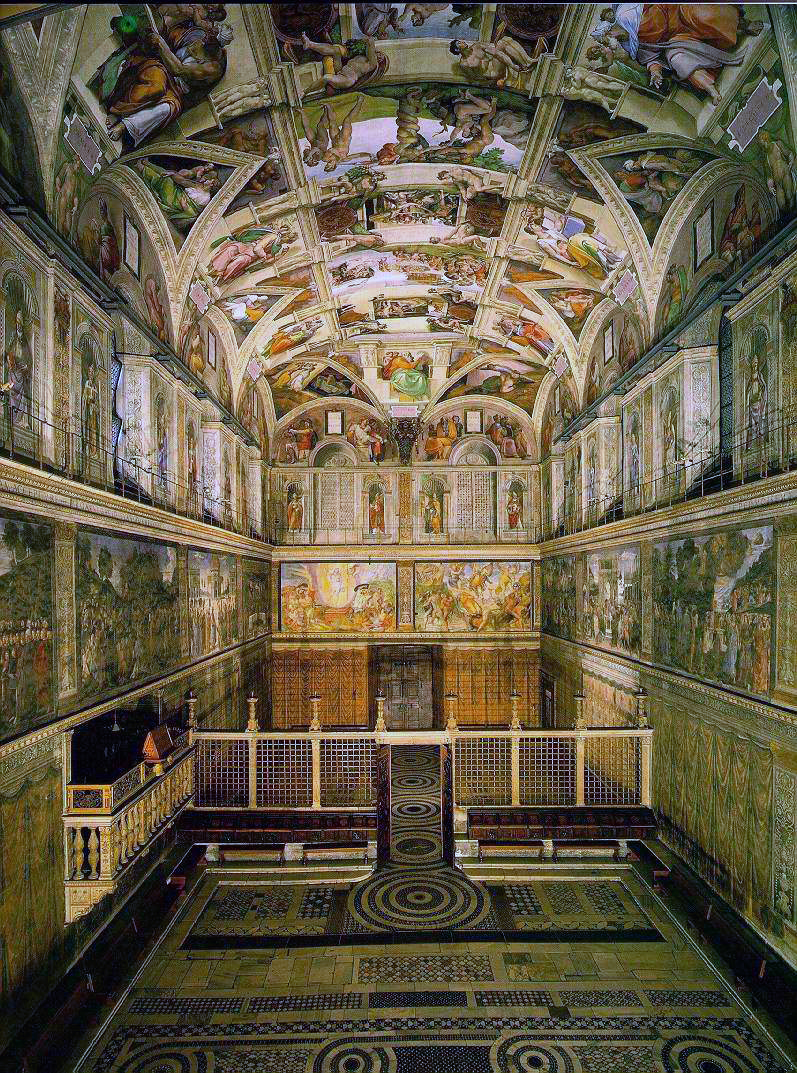

1508
Michelangelo begins Sistine Chapel
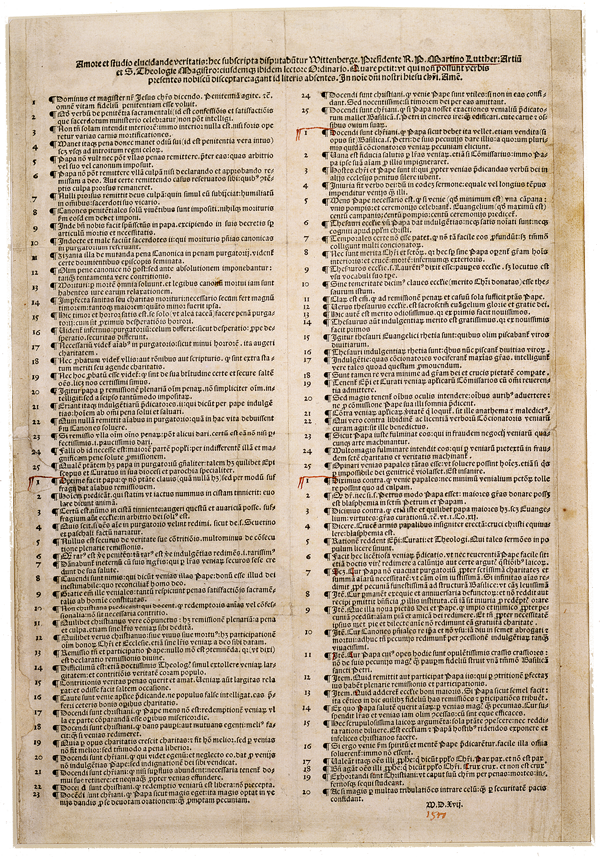
1517
Luther posts 95 Thesis
1518
Domenico Beccafumi’s mosaic of Hermes Trismegistus graced the floor of the Cathedral of Siena
1521
Luther is excommunicated
1527
1531
Church of England breaks away from Roman Catholic Church
1536
First edition of Calvin’s Institutes
1540
Jesuit order is founded
1545
Council of Trent – embodiment of the Counter-Reformation (veneration of saints, images, relics)
1550
Vasari’s ‘Lives of the Artists’
1559
The Act of Uniformity makes the 1559 Book of Common Prayer the standard for Church of England
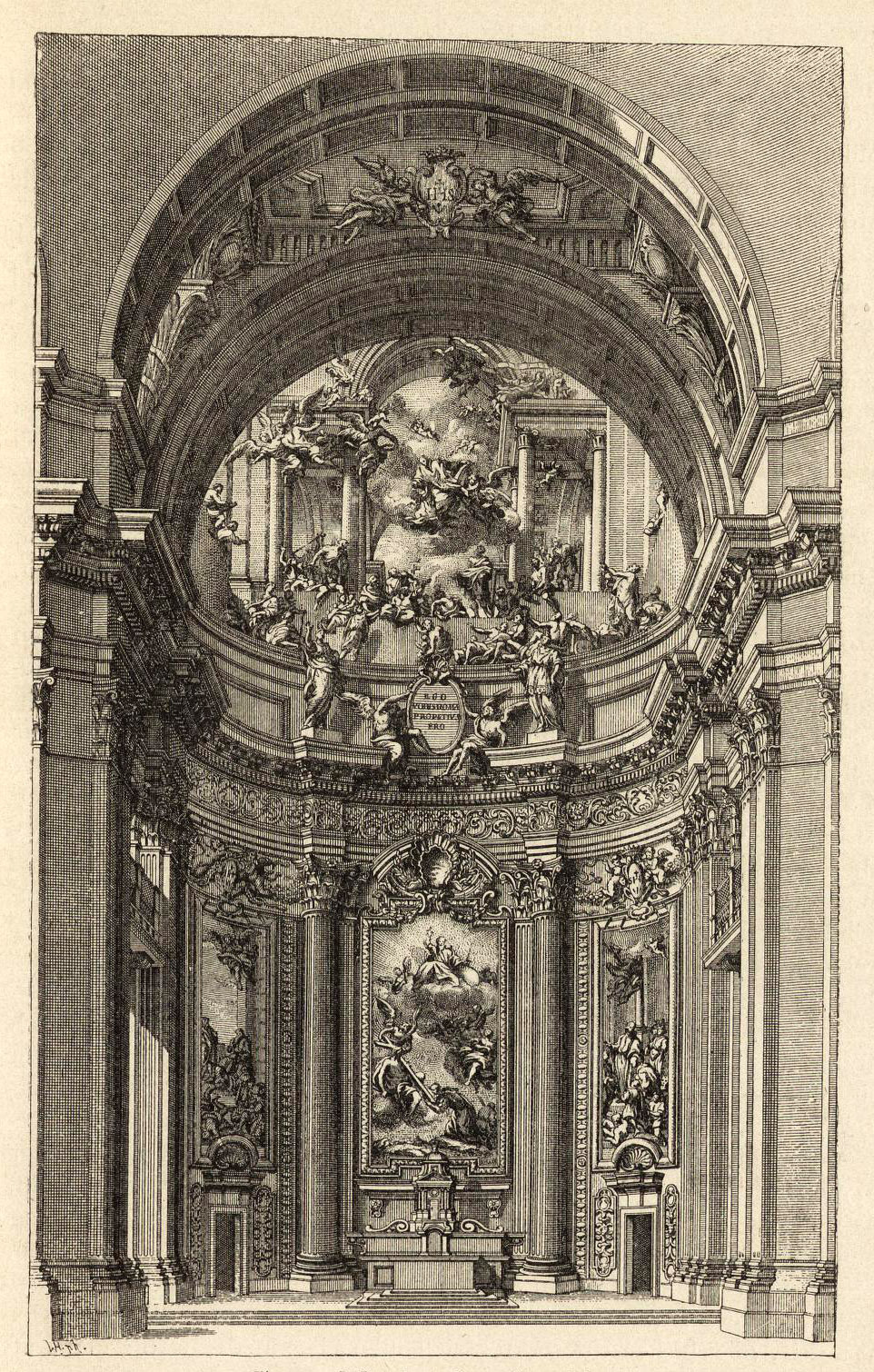
1568
Il Gesu Church, Rome
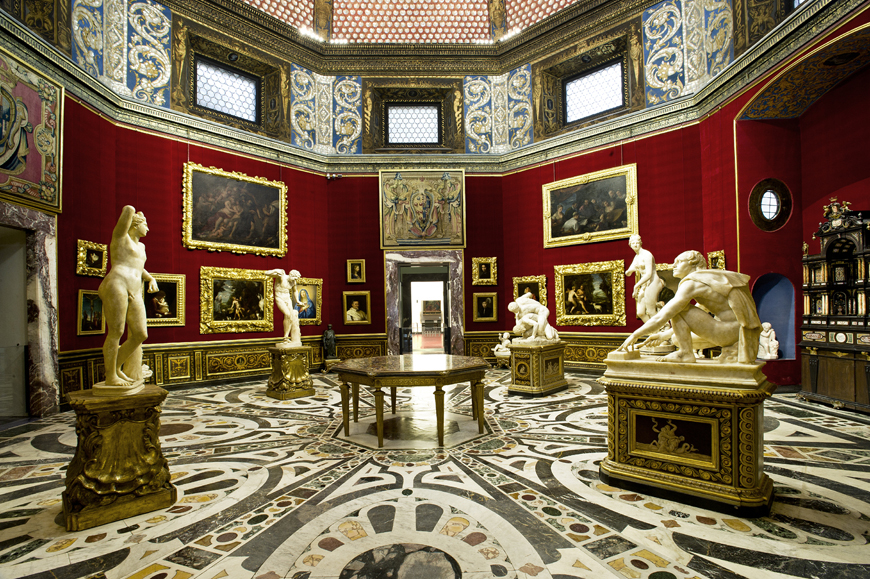

1581
Uffizi Gallery established

1628
The Gallery of Cornelius van der Geest
1633
Galileo’s trial before the Inquisition begins
1637
Descartes publishes Discourse on the Method
1667
First Salon de Paris
1671
Amerbach Cabinet opens in Basel (first and still existing public museum in the world
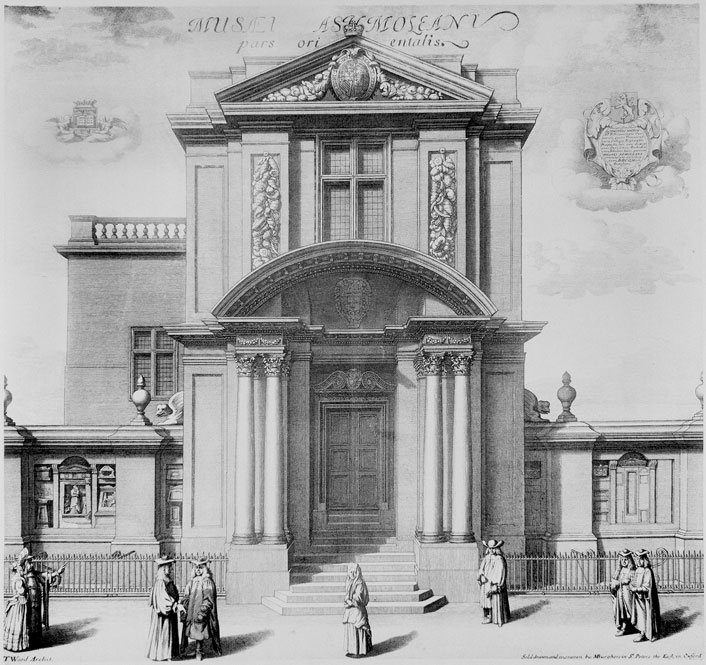

1683
Ashmolean Museum opened

1690
Cabinet of Curiosities
1694
Musèe des Beaux-Arts et d’archèologie in Besancon established after Abbot Baptiste Boisot gave his personal collection to the Benedictines in order to create a public museum
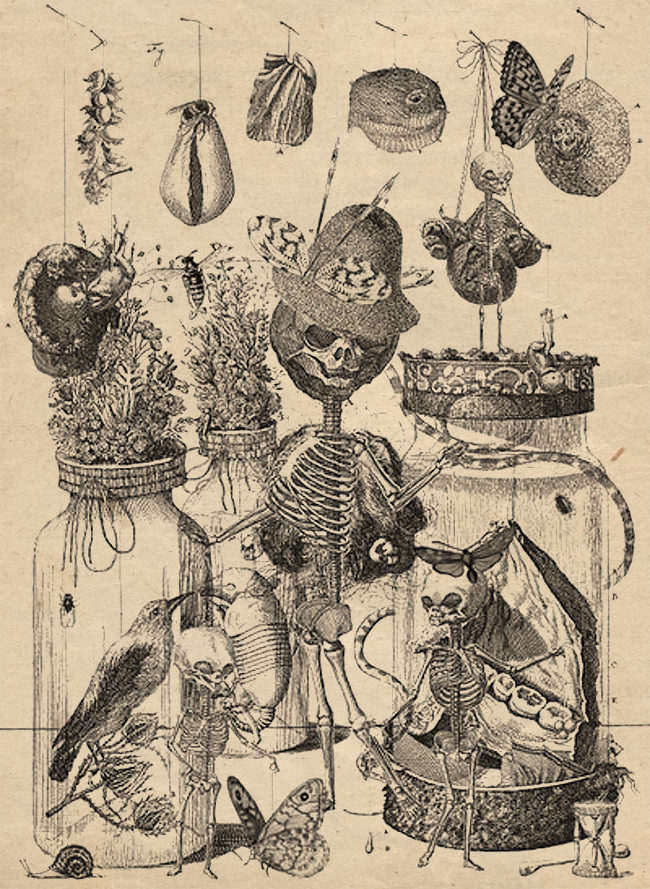
1710
Frederik Ruysch’s Museum
1727
Kunstkamera opens to the public in Kikin hall in St Petersburg
1743
Uffizi Gallery opens to the public
1748
Salon de Paris becomes the major international art event (until 1890)
1750
Gallerie dell’Accademia opens in Venice
1759
British Museum opens to the public
1764
Hermitage Collection founded by Catherine the Great – required visitors to wear gala dresses until 1866
1779
The Bavarian Royal Collection (now Alte Pinakothek) opens to the public
1781
Belvedere in Vienna opens
1785
Museo del Prado founded by Charles III of Spain
1789
Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen
1790
Kant’s The Critique of Judgement – aesthetics as an ideological function through which aesthetic judgment produces individuality
1792
Louvre opens to the ‘common people’
1797
Friedrich Schlegel described historicism as "a kind of philosophy"
1814
Dulwich Picture Gallery opens as the first purpose-built national gallery in Great Britain
1818
Mary Shelley publishes Frankenstein
1819
Museo del Prado opens to the public
1824
National Gallery London opens to the public
1830
Königliches Museum (now Altes Museum) opens
1833
Birth of Oxford Movement with publication of first edition of “Tracts for the Times”
1834
Spanish Inquisition officially ends
1848
The Communist Manifesto published
1851
1854
Doctrine of the Immaculate Conception
Lateran Museum founded by Pius IX
1855
Neues Museum opens
1856
Votivkirche (groundbreaking)
1858
St Patrick’s Cathedral, New York and St Patrick’s Cathedral Melbourne
1859
Mary Anne Schimmelpennick criticism of looking back to the dark ages
Classification of Deformities
1863
Birth of Salon des Refuses
Edouard Manet’s The Luncheon on the Grass
1869
First Vatican Council
1874
First Independent Impressionist’s Exhibition
1882
Birth of Liturgical Movement with the publication of the people’s missal at the Belgian Benedictine Abbey of Maredsous
1884
Museum of Fine Art Boston opens
1888
Paul Signet demands exhibits to be hung in a single row
1891
Kunsthistorisches Museum opens in Vienna
1895
First Venice Art Biennale
1900
Freud’s ‘Interpretation of Dreams’
1901
William James’ ‘The Varieties of Religious Experience’
1903
Pope Pius X mandated ‘‘the use of Gregorian chant by the people, so that the faithful may again take a more active part in the ecclesiastical offices, as they were wont to do in ancient times.’’
Galleria Borghese opens
Kirche am Steinhof
1906
White walls used for the Jahrhundert-ausstellung deutscher Kunst at the National Gallery in Berlin
1909
National Congress of Catholic Works in Mechelen Belgium – Cardinal Mercier called for text of the mass in vernacular language
1910
Pergamonmuseum opens
Klimt’s solo exhibition at Vienna Secession presents modern practice of white walls
1911
Kandinsky’s ‘Spiritual in Art’
1913
Freud’s Totem and Taboo
1915
Saussure’s ‘Course in General Linguistics’
1917
Duchamp submits Fountain to Society of Independent Artists Exhibition
1918
The first “community mass” at Maria Laach
1921
Romano Guardini declared the replacement of religious individualism and subjectivism with the objective, formed community
Legion of Mary founded in Dublin
1927
Heidegger’s ‘Being and Time’
1929
Museum of Modern Art founded
1932
Dornbacher Pfarrkirche
1934
Museum of Modern Art’s opening exhibition presents the white cube as the ‘international style’
C.G. Jung’s ‘Concept of the Archetype’
1936
The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction
1937
Große deutsche Kunst-ausstellung in the Haus der deutschen Kunst in Berlin bears witness to the triumph of the white exhibition wall
1938
Duchamp’s installation of bags of coal in the Exposition international du Surrealisme in Paris. Challenged the auratic single-row hanging of exhibits
1940
Hans Ansgar Reinhold recommended the maintenance of “proportionality” in the arrangement of subsidiary altars, that devotional spaces not supplant the centrality of the primary ritual.
1943
Cardinal Bertram gave Rome a comphrensive report on the origin of the Liturgical Movement
Frank Lloyd Wright designs the Solomon R. Guggenheim (built between 1956-59)
Sartre’s ‘Being and Nothingness’
1946
Roman Commission established to reform liturgical books
1947
Pope Pius XII wrote ‘Mediator Dei et Hominum,’ an encyclical on liturgical renewal and Modern art which gave both institutional and hierarchical support to the Liturgical Movement.
1949
German Bishops released a directive to remove all distractions from the interior of ritual space including side altars and Stations of the Cross.
1950
Congregation of Rites approved the German ritual; Doctrine of the Assumption of Mary
1951
First World Congress of the Catholic Lay Apostolate
Roland Barthes’ ‘Writing Degree Zero’
1955
First Documenta
Ronchamp
1958
Louisiana Museum of Modern Art established in Humlebaek
1962-65
Vatican II
Levi-Strauss’ ‘The Savage Mind’
1964
Arthur Danto’s ‘The Artworld’
Marshal McLuhan’s ‘Understanding Media’
1965
“Constitution on Sacred Liturgy”
1966
Holy Cross church, Chur
1967
Susan Sonntag’s ‘Against Interpretation’
1968
End of Modern Art
Noam Chomsky’s ‘Language and Mind’
1969
Pierre Boudie’s ‘The Rules of Art’
Adorno’s ‘Aesthetic Theory’
1972
Harald Szeeman’s documenta 5 presents the exhibition as a work of art
1973
Jack Burnham’s ‘The Structure of Art’
1976
Brian O’Doherty’s ‘Inside the White Cube’
1977
Centre Georges Pompidou opens
1981
1983
Jean Baudrillard’s ‘Simulacra and Simulation’
1984
Venice Biennale under Director Maurizio Calvesi - Luigi Nono’s Promoteo installed in disused church of San Lorenzo
1986
Friedhelm Mennekes established contemporary art program at Sankt Peter Kunst Station, Cologne
1989
1990
1994
Paul Virilio’s ‘The Vision Machine’
1995
100th anniversary of the Venice Biennale director Jean Clair opens Arsenale (formerly the home of Aperto fringe event for younger artists since 1980) and the Biennale expands beyond Giardini
1996
First Manifesta
1998
Nicolas Bourriaud’s ‘Relational Aesthetics’
2001
Lev Manovich’s ‘The Language of New Media’
2004
Miwon Kwon’s “One Place After Another”